Turbulent heat fluxes during an extreme lake effect snow event
Abstract
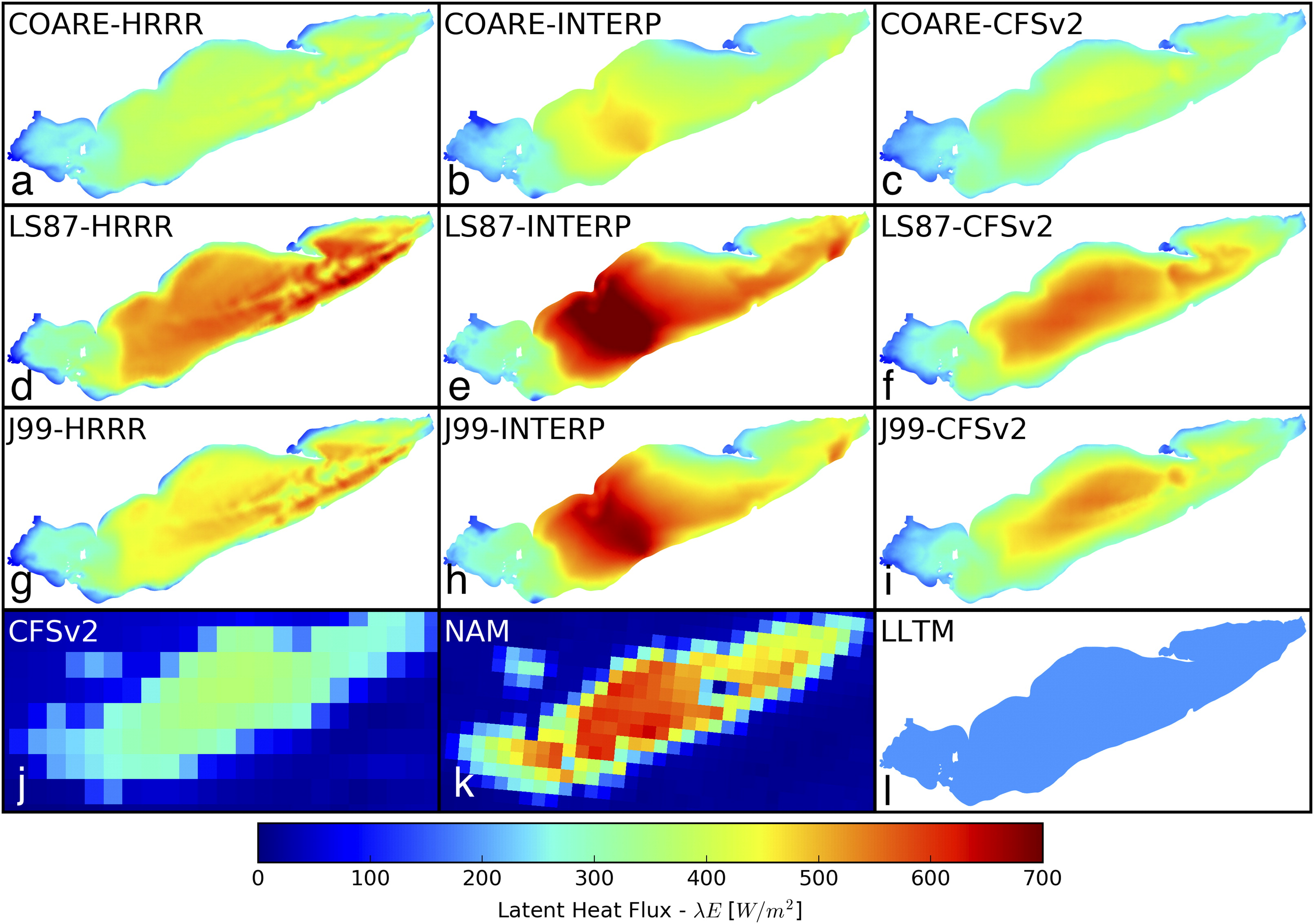
Proper modeling of the turbulent heat fluxes over lakes is critical for accurate predictions of lake-effect snowfall (LES). However, model evaluation of such a process has not been possible because of the lack of direct flux measurements over lakes. The authors conducted the first-ever comparison of the turbulent latent and sensible heat fluxes between state-of-the-art numerical models and direct flux measurements over Lake Erie, focusing on a record LES event in southwest New York in November 2014. The model suite consisted of numerical models that were operationally and experimentally used to provide nowcasts and forecasts of weather and lake conditions. The models captured the rise of the observed turbulent heat fluxes, while the peak values varied significantly. This variation resulted in an increased spread of simulated lake temperature and cumulative evaporation as the representation of the model uncertainty. The water budget analysis of the atmospheric model results showed that the majority of the moisture during this event came from lake evaporation rather than a larger synoptic system. The unstructured-grid Finite-Volume Community Ocean Model (FVCOM) simulations, especially those using the Coupled Ocean–Atmosphere Response Experiment (COARE)-Met Flux algorithm, presented better agreement with the observed fluxes likely due to the model’s capability in representing the detailed spatial patterns of the turbulent heat fluxes and the COARE algorithm’s more realistic treatment of the surface boundary layer than those in the other models.